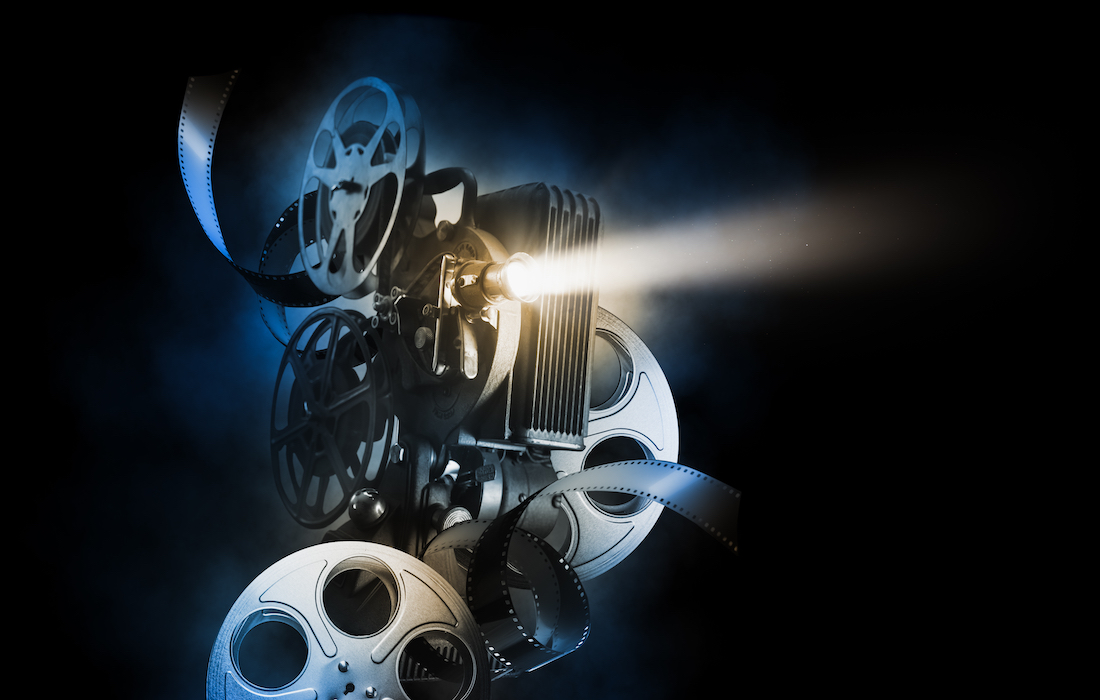
Tremendous televisions and home theaters managed to be an authentic gratification. But in the last few years, numerous people possess to begun to view huge screens including exceptional pictures as essential for watching TV and movies at home. Although old-traditional home ray tube (CRT) TVs posterior produces a magnificent picture, they can’t maintain the screen size that people look for today. Projection TVs can produce a mythical bigger picture than CRT sets can, and front and rear projection models can suit a variety of places and resources.
An immeasurable way to learn how a projection TV works is to resemble it to a standard TV. A standard television uses a cathode beam tube (CRT) to generate a picture.
A CRT discharges a ray of negatrons at a phosphor-coated screen. Every time an electron comes into connection with the screen, such a point, is called a pixel, gleams. Brilliance CRT televisions use three electron lasers and separate phosphors for red, green and blue. When you watch, you’re staring directly at the facade that the TV uses to generate the image. That’s why conventional CRT sets are called direct view ostentations.
CRTs remain extremely reliable and produce good image quality. But they do have one influential disadvantage since the screen is made of glass, size is restricted. The most extensive CRT screens estimated about 40 inches diagonally.
That’s the foremost understanding of projection TVs. Even though some models can’t challenge the essence of a direct-view CRT set, they can be much larger. Instead of utilizing a direct-view setup, a projection TV creates a miniature picture and then uses a ray of enlightenment to demonstrate that picture at a much more substantial proportion.

There are two main configurations in Projection TVs front projection and rear projection.
A front projection model uses a projector and a separate screen, and it projects pictures onto the front of that screen. This plan looks most like what you’d find in a movie multiplex, the projection assembly is entirely separate from the screen. The projector can be installed on a table or installed on the dome. The image looks most reliable while presented on a high-quality screen, but a specifically painted, flat wall will work well.
Rear projection systems look more like traditional televisions. They present pictures on the back of a screen fairly than the front, and the projector is totally included inside the television itself. You can also set up a rear-projection system with a projector and a specific screen, but the term is most frequently utilized to explain self-independent sets.
Both configurations use miniature machines competent in performing extremely accurate images. Certain devices can be contemplative, indicating that light chooses up the image by leaping off the device. Or, they can be transmissive, determining that light picks up the picture by traveling through the device. Once the light picks up the picture, a lens magnifies the picture and projects it over the screen.
Next, we’ll take a gander at the main varieties of television technologies and how they relate to one another.
The transmissive projection types carry CRTs and liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Hereabouts a summary view of how to control work:
CRT: A CRT projector uses much more diminutive tubes than conventional television. These tubes produce the picture in the identical way a regular TV does by arousing electrons at a phosphor-coated screen. A CRT projector can include:
- One colored CRT with green, red and blue phosphors
- One black and white CRT and a spinning color roller that combines the color
- One each for green, red and blue CRT’s
Liquid crystal display (LCD) Electrical flows can cause liquid crystals to improve their appearance. This enables them to perform as light valves varying amounts of current permit various masses of light to cross through each crystal. This lets the LCD device produce a greyscale picture. To combine intensity, most projectors utilize a range of mirrors that split the light into green, red and blue beams. Each beam crosses within a separate LCD, and a lens assembles the three rays and projects the reflection on the screen. LCDs can also be practiced to create flat-panel televisions.